MicroPython on ESP32
Contents
- 1 About
- 2 Do not forget
- 3 ESP32
- 4 Meeting notes
- 4.1 1. Connect on the serial console
- 4.2 2. Read the help()
- 4.3 3. Identify your version
- 4.4 4. Blink the LED (pin22)
- 4.5 5. Look at the Quick Reference for ESP8266
- 4.6 6. Try to connect to the WIFI
- 4.7 7. Install a package with UPIP
- 4.8 8. Upgrade your firmware
- 4.9 9. Create a website with picoweb
- 4.10 10. Use an ESP8266 as a serial adaptor
- 5 Registration
- 6 Board reservations
- 7 Notepad
- 8 Links
About[edit]
Let' play around with micropython on the ESP32, in our case the 'Lolin32 lite' boards.
MicroPython is a interpreter for the Python language dedicated to Microcontrollers, making easier for everyone to play with microcontrollers.
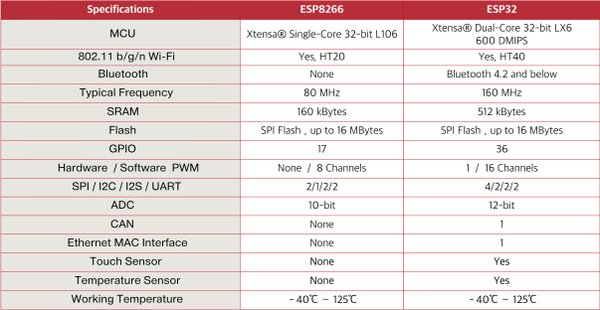
ESP32 is a new powerful microcontroller with Wifi and Bluetooth on board, perfect to play with the IoT.
Do not forget[edit]
- laptop
- microusb cable
- breadboard (optional)
- leds (optional)
- arduino modules (optional)
ESP32[edit]
The ESP32 is the successor of the ESP8266, with bluetooth, more memory and a higher frequency.
Meeting notes[edit]
1. Connect on the serial console[edit]
Linux:
1. install screen 2. ls /dev/ttyUSB0 3. screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200 4. you should get a prompt: >>> >>> 5. you can also use python itself to access the serial console $ python -m serial.tools.miniterm /dev/ttyUSB0 115200 --- Miniterm on /dev/ttyUSB0 115200,8,N,1 --- --- Quit: Ctrl+] | Menu: Ctrl+T | Help: Ctrl+T followed by Ctrl+H --- >>>
Windows:
4. putty: http://store.chipkin.com/articles/using-putty-for-serial-com-connections-hyperterminal-replacement
OSX: use screen as well
1. screen /dev/tty.wchusbserial1410 115200
2. Read the help()[edit]
>>> help() Welcome to MicroPython on the ESP32!
For generic online docs please visit http://docs.micropython.org/
For access to the hardware use the 'machine' module:impor
import machine pin12 = machine.Pin(12, machine.Pin.OUT) pin12.value(1) pin13 = machine.Pin(13, machine.Pin.IN, machine.Pin.PULL_UP) print(pin13.value()) i2c = machine.I2C(scl=machine.Pin(21), sda=machine.Pin(22)) i2c.scan() i2c.writeto(addr, b'1234') i2c.readfrom(addr, 4)
Basic WiFi configuration:
import network
sta_if = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF);
sta_if.active(True)
sta_if.scan() # Scan for available access points
sta_if.connect("<AP_name>", "<password>") # Connect to an AP
sta_if.isconnected() # Check for successful connection
Control commands:
CTRL-A -- on a blank line, enter raw REPL mode CTRL-B -- on a blank line, enter normal REPL mode CTRL-C -- interrupt a running program CTRL-D -- on a blank line, do a soft reset of the board CTRL-E -- on a blank line, enter paste mode
For further help on a specific object, type help(obj) For a list of available modules, type help('modules') >>>
3. Identify your version[edit]
>>> import sys >>> sys.implementation (name='micropython', version=(1, 9, 2)) >>> sys.version '3.4.0' >>>
4. Blink the LED (pin22)[edit]
>>> import time
>>> from machine import Pin
>>> led=Pin(22,Pin.OUT)
>>> while True:
led.value(1)
time.sleep(0.5)
led.value(0)
time.sleep(0.5)
Then you should have the LED blinking...
5. Look at the Quick Reference for ESP8266[edit]
This quick reference is for a less-powerful chip from the same company, but most instructions should work the same.
https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/esp8266/esp8266/quickref.html
6. Try to connect to the WIFI[edit]
>>> import network
>>> wlan = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF) # create station interface
>>> wlan.active(True) # activate the interface
>>> wlan.scan() # scan for access points
>>> wlan.isconnected() # check if the station is connected to an AP
>>> wlan.connect('HSBXL', 'CLUBMATE2010') # connect to an AP
>>> wlan.config('mac') # get the interface's MAC adddressµ
>>> wlan.ifconfig() # get the interface's IP/netmask/gw/DNS addresses
('172.23.187.115', '255.255.255.128', '172.23.187.1', '172.23.187.1')
>>> ap = network.WLAN(network.AP_IF) # create access-point interface
>>> ap.active(True) # activate the interface
I (2892816) wifi: mode : sta (30:ae:a4:4e:84:a8) + softAP (30:ae:a4:4e:84:a9)
I (2892816) wifi: pm stop, total sleep time: 0/97419646
True
I (2892826) wifi: event 13
ap.config(essid='ESP-AP') # set the ESSID of the access point, you should be able to see this new Wifi network from your laptop...try to ping it from your laptop: $ ping 172.23.187.115
7. Install a package with UPIP[edit]
>>> import upip
I (3929506) modsocket: Initializing
>>> upip.install('micropython-telnetlib')
Installing to: /lib/
Installing micropython-telnetlib 0.0.1 from https://pypi.python.org/packages/22/0a/ae956d478b893a0d170fc66f781c880249a44fee930fde5f18b440e754c8/micropython-telnetlib-0.0.1.tar.gz
This is just to show that you can install a library, not very useful except to test that you can install something.
8. Upgrade your firmware[edit]
Just read the documentation on : https://micropython.org/download
But in brief, pip install esptools --user You will have a esptools.py file in your ~/.local/bin/ directory from the download page, you can find the last version of the firmware for esp32, http://micropython.org/resources/firmware/esp32-20180224-v1.9.3-362-g2ad555bc.bin
before the upgrade, just disconnect your terminal session to the esp32 download it and just apply it with esptools.py
example:
esptools.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 write_flash -z 0x1000 esp32-20180224-v1.9.3-362-g2ad555bc.bin
get the esptools for python
$ sudo apt install python-pip $ sudo pip install --upgrade pip $ sudo pip install esptool --upgrade
Next, you have to erase the old firmware!
$ esptool.py --port /dev/ttyUSB0 erase_flash
Then flash the new firmware: $ esptool.py --chip esp32 --port /dev/ttyUSB0 write_flash -z 0x1000 newfirmware.bin
9. Create a website with picoweb[edit]
>>> import upip
>>> upip.install('picoweb')
>>> def index(req, resp):
... yield from resp.awrite('HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n')
... yield from resp.awrite('Content-Type: text/html\r\n')
... yield from resp.awrite('\r\n')
... yield from resp.awrite('I can show something to zoobab')
...
...
...
>>> app = picoweb.WebApp(__name__, [('/', index)])
>>> app.run(debug=True, host='0.0.0.0')
* Running on http://0.0.0.0:8081/
10. Use an ESP8266 as a serial adaptor[edit]
https://www.cnx-software.com/2017/10/16/esp32-micropython-tutorials/
Registration[edit]
We have 20 Lolin32 boards in stock for participants.
Please register here:
https://www.meetup.com/hackerspace-Brussels-hsbxl/events/247897619
Board reservations[edit]
Please add your name to the list below if you want us to keep a Lolin32 for you:
- betz
- Polyglot
- Nino
- George (via Ugo)
- Blazej (via Ugo)
- Olivier (D.)
- Ali (via Ugo)
- Jacopo (via Ugo)
- Jason Friel
- Bob (gratefulfrog)
- [You ?]
Boards not reserved will be available during the workshop, but first-come first-served ;-)
Notepad[edit]
https://etherpad.openstack.org/p/Micropython-esp32
Links[edit]
- http://nick.zoic.org/talk/lca2017/
- https://hackernoon.com/get-on-the-good-foot-with-micropython-part-2-e1f2efaad50b
- http://www.buildlog.net/blog/2018/02/game-audio-for-the-esp32/
- https://github.com/mcauser/BLUE_PILL_F103C8
- https://fr.aliexpress.com/item/LOLIN32-Lite-V1-0-0-WIFI-Bluetooth-Conseil-de-D-veloppement-Bas-ESP-32-ESP32-CH340/32844514398.html
- https://badge.sha2017.org/
- https://github.com/zoobab/micropython-alpine
- https://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/esp8266/esp8266/quickref.html (for another chip, should work mostly the same)
- https://www.cnx-software.com/2017/10/16/esp32-micropython-tutorials/